A search query is the precise combination of words a user types or speaks into a search engine to seek information.
Search queries are the exact words and phrases people use, while keywords are the specific terms marketers derive from these queries to pinpoint the main topic a user is exploring. Users can input search queries in various ways, such as:
- Typing directly into search bars, like those on Google or a web browser.
- Speaking their queries into voice search tools, such as Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant.
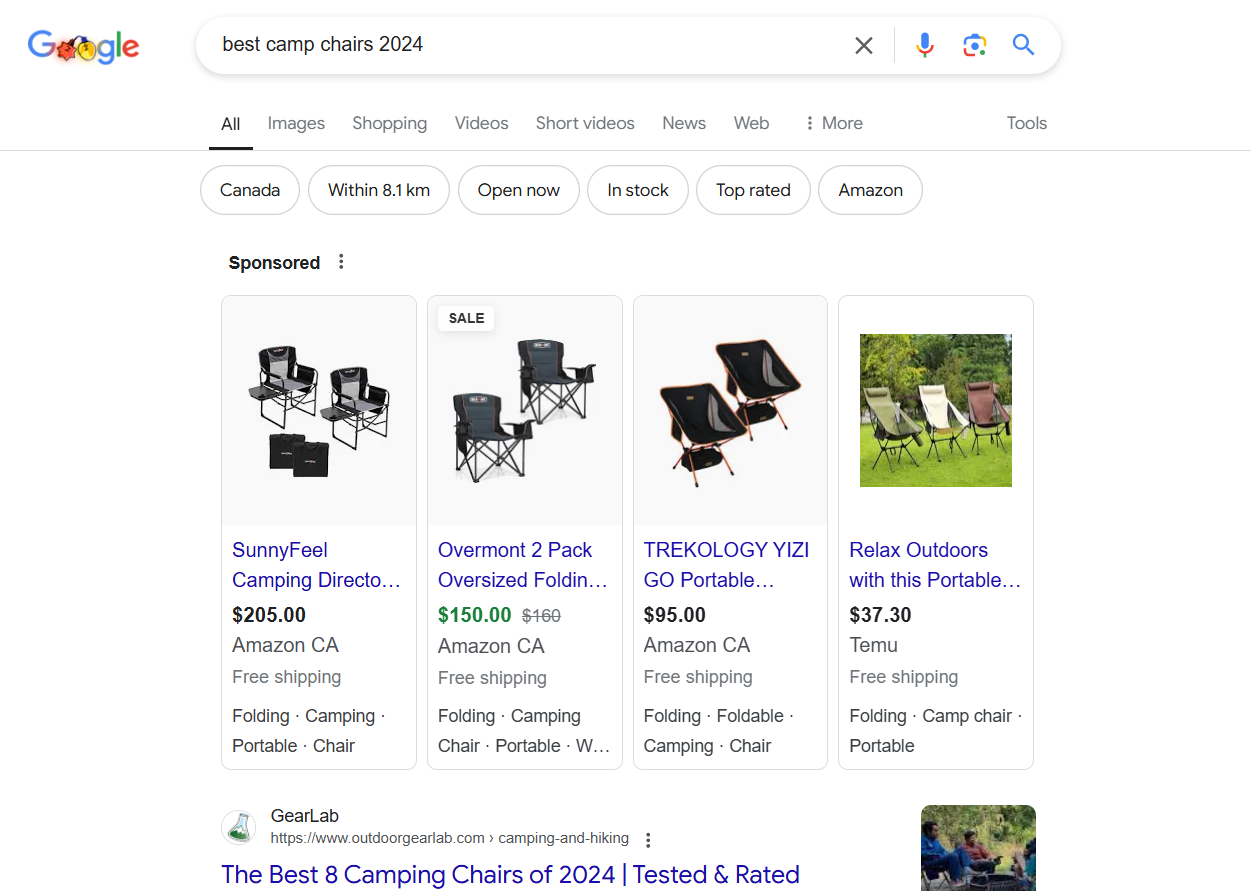
Search engines like Google and Bing process these queries and deliver the most relevant results on search engine results pages (SERPs), considering factors like user intent, relevance, and context. For instance, here’s the SERP for the query “best camp chairs 2024.”
While search queries often contain keywords, the two terms are not interchangeable. Both are essential for understanding your audience’s needs and crafting content that aligns with their intent.
For instance, someone searching for camp chairs might enter queries like:
- What are the best camp chairs
- Comfy camp chairs to buy
- Cheap camp chairs near me
- Modern green-colored camp chairs
In these examples, the broad keyword is “camp chairs.” However, this keyword alone doesn’t reveal specific user intent. By analyzing detailed search queries, you can uncover what users truly want and tailor your content accordingly.
Search Query Types
Google search queries are generally categorized into four main types, each reflecting different user intent. Understanding these types is essential for creating targeted content that aligns with what users are searching for. Here’s a breakdown:
- Informational Queries
These are used when users seek knowledge, facts, or guidance without a specific action in mind. The intent is purely to gather information.
Examples:
-
- “How to tie a tie”
- “What is the capital of France?”
- “Benefits of regular exercise”
If you carefully examine the above examples, you will notice that there is no immediate intent to purchase or perform an action. Hence, the content like blogs, tutorials, and informational articles performs well here.
- Navigational Queries
In this kind, users enter these queries to find a specific website, brand, or resource. They already know where they want to go but use Google to get there.
Examples:
-
- “Facebook login”
- “Amazon customer service”
- “OpenAI website”
In this type, users already have a clear destination in mind. So, the SEO strategies should focus on ensuring your website ranks high for your brand name and related terms.
- Transactional Queries
These queries indicate that the user is ready to take action, such as making a purchase, signing up for a service, or downloading something. The intent is to perform a specific action.
Examples:
-
- “Buy Nike running shoes”
- “Subscribe to Netflix”
- “Download free PDF editor”
This type Indicates high intent to convert which is ideal for product pages, pricing pages, and promotional offers. This query also reflects the user behaviour that he/she has done the research and reached at the last stage of purchase.
- Commercial Investigation Queries
These queries show that the user is considering a purchase or action but wants to explore options and compare before making a decision. The intent is to research products, services, or solutions.
Examples:
-
- “Best smartphones under $500”
- “Top-rated coffee makers”
- “Comparison between iPhone and Samsung Galaxy”
This reflects that users are in the research phase of their decision-making process. Detailed reviews, comparison guides, and case studies work well to capture this audience.
These search queries are basically the intent of online search. It means that search queries reflect the purpose or goal behind a user’s online search. When someone types a query into a search engine, it reveals what they are looking for—whether it’s information, a specific website, or a product or service to purchase.
How to implement Search Queries in SEO and PPC Campaign
Effectively targeting search queries is critical for successful SEO and PPC campaigns, as it helps drive the right audience to your website while maximizing your return on investment (ROI). Here’s a detailed breakdown of how to target search queries in these campaigns:
Understand Your Audience
- Buyer Personas: Develop detailed buyer personas to understand your audience’s needs, interests, and behaviors.
- Search Intent: Determine whether users are looking for information (informational), comparing options (navigational), or ready to buy (transactional). Tailor your strategy accordingly.
Make your content people-first not search engine first.
If a search query contains a keyword your webpage is optimized for, Google may rank your page in the SERPs. Which could result in the user clicking through to your website.
Perform Comprehensive Keyword Research
This process includes analyzing search volume, competition, and user intent to uncover keywords that drive traffic and conversions. Using tools like Google Keyword Planner or SEMrush, you can find primary keywords, long-tail variations, and gaps in competitor strategies. This research forms the foundation of effective SEO and PPC campaigns, ensuring your content and ads align with user searches.
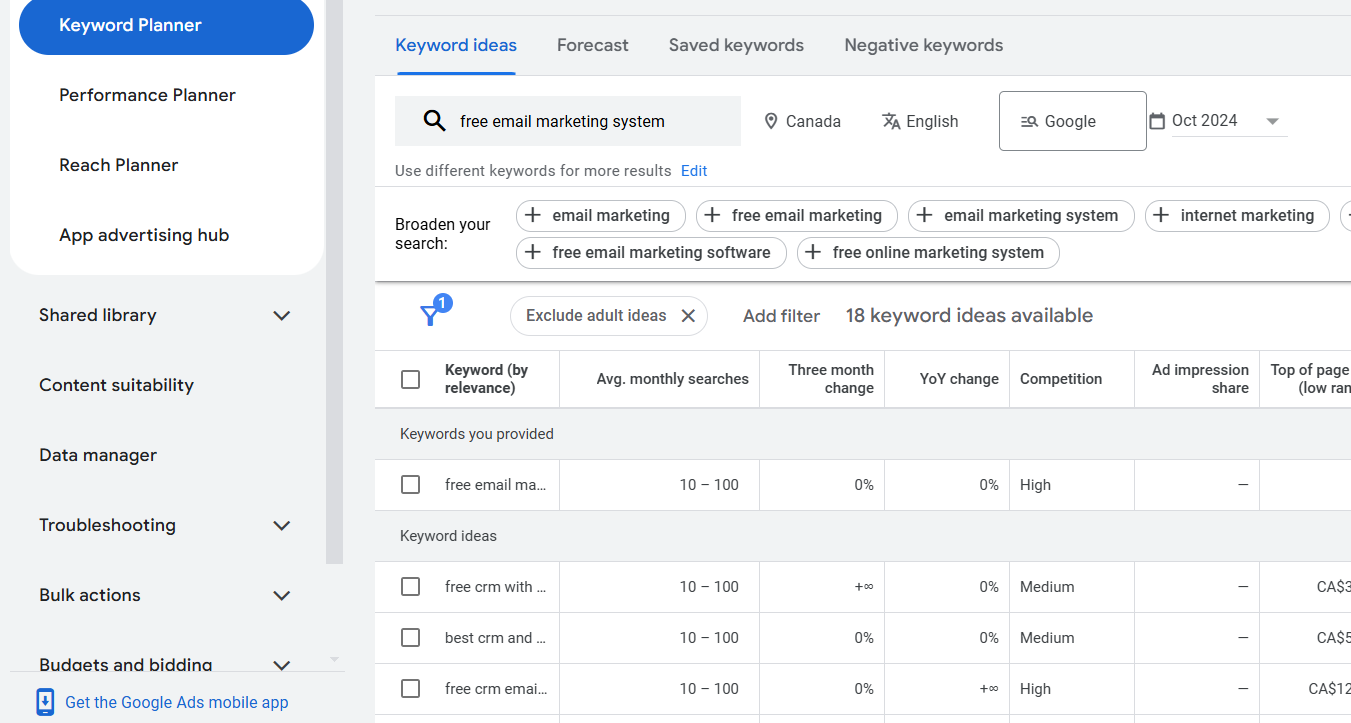
To optimize a page for a keyword, add it to on-page elements like the following:
Title tag: An HTML element that gives a title to a webpage
Meta description: An HTML element that provides a short summary of a webpage
URL: The address of a webpage that a user sees in their web browser
Then, add related keywords, long-tail keywords subtopics, and questions to the headings and body copy of your page.
Tools: Tools such as Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Ubersuggest can be used to identify high-value keywords.
Long-Tail Keywords: Focus on long-tail keywords as they often have less competition and higher conversion potential.
Competitor Analysis: Analyze your competitors’ keywords to identify gaps and opportunities in your strategy.
Optimize Landing Pages
SEO: Ensure each landing page is optimized for search query with targeted keywords in the title, headers, meta descriptions, and content.
PPC: Align ad copy and landing page content with search intent to improve Quality Scores and conversion rates.
Create Compelling Ad Campaigns for PPC
Keyword Match Types: Use broad match, phrase match, and exact match keywords strategically.
Negative Keywords: Add irrelevant or low-converting keywords to your negative keyword list to avoid wasted spend.
Ad Extensions: Enhance visibility with site links, callouts, and structured snippets.
Monitor and Adjust Based on Performance
SEO Metrics: Track organic traffic, bounce rates, time on page, and keyword rankings.
PPC Metrics: Analyze CTR, conversion rates, cost-per-click (CPC), and ROI.
A/B Testing: Continuously test variations in ad copy, landing pages, and keywords for optimization.
Leverage Local and Voice Search
Local SEO: Optimize for location-based queries by targeting “near me” keywords and updating Google My Business.
Voice Search: Incorporate natural language and question-based keywords to capture voice search traffic.
Targeting the right search query is essential for connecting with your ideal audience and achieving meaningful results in SEO and PPC campaigns. Additionally, refining your approach with tools, competitor insights, and ongoing performance analysis ensures your strategy remains effective and cost-efficient, ultimately driving qualified traffic and boosting conversions.